Approaches to gender in advertising are shaped by social patterns that continue to evolve. How can you effectively use knowledge about gender differences so that gender marketing helps build lasting customer relationships and boost sales? Can eliminating gender stereotypes in advertising and promotion in favor of equality-based messages bring benefits to a company? This article explores these questions.
Definition and Fundamentals of Gender Marketing

Gender marketing – is an approach that takes into account the differences between women and men in marketing strategies. It focuses on creating and communicating an offer that aligns with the expectations and needs of both genders.
The analysis of decision-making processes and consumer needs, including those of women, plays a key role here. Effective gender marketing recognizes the role of a product in meeting a customer’s needs and personalizes communication by using emotions to build relationships. Different communication codes are used in marketing messages to better tailor communication to women and men, female and male consumers. Through gender marketing, a brand can build stronger relationships with diverse audience groups.
What Is Gender-Targeted Marketing?
Gender-targeted marketing focuses on tailoring products, services, and marketing communication to the specific traits and preferences of male or female target groups. Its goal is to reach audiences more effectively, build customer loyalty, and eliminate gender stereotypes in marketing messages.
First Steps in Gender Marketing: From Theory to Practice
To effectively apply gender marketing, it’s necessary to understand the differences in expectations and behaviors of both genders in the context of their purchasing preferences, lifestyle, and responses to advertising. At this stage, it’s worth analyzing consumer decision-making processes to better adapt the strategy to their needs. Then, apply this knowledge in practice by creating target groups to which messages and communication can be personalized.
It’s important that, when taking the first steps in gender marketing, you don’t reinforce harmful gender stereotypes. Instead, promote equality and diversity. This also requires monitoring social trends and adapting to changing norms and consumer attitudes toward gender. Analyzing the effects of marketing activities allows you to evaluate how effectively business goals are being met and provides opportunities for further strategy optimization.
Aspects of Cultural and Biological Gender and Consumer Behavior
Biological sex plays an important role in shaping consumer behavior and is one of the basic criteria for market segmentation in marketing. In practice, this means that women and men often demonstrate different preferences, needs, and expectations regarding products and services.
Biological sex – example of behaviors:
Women may pay more attention to the emotional aspect of a purchase, the relationship with the brand, or the values represented by a given product.
Men, on the other hand, tend to focus more on functionality, quality, and the practical aspects of use.
In the context of gender marketing, understanding these differences is essential for effectively reaching consumers and building lasting customer relationships. Remember that the consumer’s gender affects not only product choices but also:
- the way advertising messages are perceived,
- preferred communication channels,
- purchasing decisions made under the influence of emotions or rational arguments.
Recently, however, there has been a clear trend away from rigid gender divisions in marketing. More and more brands are focusing on diversity and inclusivity, creating campaigns that move beyond traditional gender roles. Modern marketing increasingly refers to universal values such as authenticity, freedom of choice, and individuality, instead of reinforcing stereotypes about biological sex.
In practice, this means that effective gender marketing requires not only an understanding of the differences between biological and cultural gender but also the ability to respond flexibly to changing social expectations. Brands that can adapt their strategies to current trends and consumer needs gain a competitive advantage and build a positive image in the eyes of customers.
It’s worth remembering that a consumer’s gender is only one of many factors influencing purchasing behavior. The key to success in gender marketing lies in combining knowledge of biological and cultural gender with a deep understanding of the audience’s values, motivations, and lifestyle. Only then is it possible to create messages that are authentic, engaging, and effective—regardless of gender.
Differences Between Gender Marketing and Gendered Marketing
Gender marketing is a strategy that distinguishes the needs of men and women, while gendered marketing may involve reinforcing gender stereotypes through marketing. The latter practice is increasingly being abandoned, as the approach to gender in marketing has changed significantly in recent years. This shift is mainly due to the widespread recognition of negative stereotypes and the gradual evolution of habits and attitudes.
Example: Car commercials traditionally aimed at men and deodorant ads targeted at women show how approaches differ in gendered marketing, while modern campaigns increasingly break these patterns.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Gender Marketing

Whether gender marketing has advantages or disadvantages depends on how it’s applied. Striking a balance between adapting to gender differences and avoiding the reinforcement of harmful stereotypes or exclusion of specific consumer groups is a challenge. However, it’s worth the effort, as the potential benefits are encouraging. Analyzing the results of marketing activities is a key element in evaluating effectiveness, allowing for strategy optimization and better message alignment.
The success of gender marketing depends on the ability to adapt to societal expectations and shifts in social structure.
Benefits of Applying Gender Marketing
The advantages of gender marketing include:
- Better understanding of men’s and women’s preferences and needs, allowing for more tailored products and marketing communication for specific target groups.
- Gender-tailored campaigns can help build stronger relationships with customers.
- Personalized messages are more aligned with the tastes and expectations of a specific target group, increasing the effectiveness of marketing campaigns.
- Consciously eliminating gender stereotypes promotes equality and diversity values, which can attract attention and social recognition.
- Analyzing gender differences can lead to the creation of innovative products that meet the specific expectations and needs of men and women.
Criticism and Potential Risks of Gender Marketing
Where do the drawbacks of gender marketing come from? Criticism mainly focuses on the risk of reinforcing gender stereotypes that can be socially harmful. Some campaigns may generate controversy and harm a brand’s reputation if they don’t align with current social norms regarding consumer gender.
Marketing targeted solely by gender can lead to oversimplifications and generalizations. It’s important to emphasize that reactions to marketing messages differ not only by gender but also by individual traits such as interests or customer needs. Ignoring individual differences within a gender group risks excluding those who don’t feel represented in any campaign. Focusing on gender as the only segmentation criterion can result in underestimating other important characteristics and preferences.
Example: Toys “R” Us decided to eliminate gender-based divisions in its toy sections. After all, girls can play with Hot Wheels cars, and boys can play with Barbie dolls.
Strategies and Tools in Gender Marketing
Should we base our gender marketing strategies solely on gender? Not necessarily. Effective gender marketing requires understanding gender differences, cultural awareness, and the ability to adapt marketing messages to diverse groups.
How to create effective gender marketing strategies:
- Start with analysis – conduct market research to understand purchasing preferences, consumer habits, and gender-related values. Use this data to identify clearly defined target groups.
- Adapt marketing content to match the expectations and needs of specific gender groups.
- Run marketing campaigns targeted at specific audiences, using communication channels preferred by each gender.
- Avoid reinforcing harmful gender stereotypes in advertising and promotion. Incorporate values related to equality and diversity, as well as elements of social responsibility. Engage in gender equality initiatives and promote inclusion by taking active steps to reshape marketing messages that redefine gender roles.
- Stay up to date with social trends related to gender to keep strategies aligned with the changing cultural context.
Gender Marketing Mix: Key Elements

Just like the traditional marketing mix known as the 4Ps (product, price, place, promotion), the gender marketing mix includes these elements and adapts them to gender differences.
Product: designing products that meet the specific needs of men and women; developing innovative solutions based on gender analysis. The product plays a central role in meeting the needs of both genders, serving as the key element of the decision-making and purchasing process.
Price: adjusting pricing strategies for different gender groups, taking into account varying levels of price sensitivity, and creating discounts or promotions that appeal to specific gender audiences.
Place: ensuring product availability in locations that are attractive to a particular target group.
Promotion: creating advertising and promotional messages tailored to different gender groups, using diverse models, characters, and scenarios while eliminating harmful stereotypes.
The Role of Gender in Advertising and Marketing
Advertising has a huge influence on shaping brand, product, and communication identity. Whether a campaign relies on gender stereotypes or promotes equality and diversity can significantly impact brand image. Through advertising, brands increasingly portray a modern image of men—moving away from traditional stereotypes and emphasizing the multidimensional nature of their social roles.
Today, advertising and marketing strive to avoid limiting stereotypes and instead aim for equality and diversity. This helps build a positive brand image in a gender-diverse society. Companies aware of these dynamics are better able to meet the expectations of modern consumers.
Example: A company that humorously uses masculine traits is Old Spice with its campaign “The Man Your Man Could Smell Like.” These ads play on traditional ideas of masculinity while attracting attention through originality.
Gender Marketing and Consumer Communication
Effective communication requires understanding how different genders process and respond to marketing messages. Gender marketing in communication helps tailor messages to gender preferences and deliver more effective outreach. Recognizing customers’ needs and expectations is crucial for personalizing communication and improving its effectiveness.
Conscious use of gender marketing can help eliminate harmful gender stereotypes, which is essential for building a positive brand image. Companies can communicate with consumers by highlighting values related to gender equality and by actively engaging in social issues related to gender.
Gender Marketing and Gender Stereotypes

There is a risk that gender marketing may unintentionally reinforce stereotypes, which is why a conscious and ethical approach is essential. It’s important to view gender holistically—encompassing both biological and cultural aspects—so that communication is more consistent and aligned with real audience needs.
The Role of Gender-Neutral Branding in Breaking Stereotypes
Gender-neutral branding involves creating brands and marketing campaigns in ways that avoid stereotypical associations with rigid gender norms. Instead, it focuses on universal values and needs. This approach also includes:
- Promoting diversity – emphasizing that products are universal and not tied to gender,
- Challenging beliefs about the dominance of one gender over another,
- Eliminating stereotypes related to body image, beauty, and social roles.
Gender-neutral marketing seeks to change social perceptions of gender, encouraging a more flexible and open view of human differences. Society plays a major role here, as it shapes gender norms and expectations and influences consumer decision-making. Brands that embrace this direction can enhance their reputation and connect with consumers who value equality and inclusion.
Example: Google’s “Made with Code” initiative encourages coding education regardless of gender.
Marketing Femininity and Marketing Masculinity: Two Sides of the Same Coin
Marketing femininity and marketing masculinity are strategies opposite to gender-neutral marketing. They focus on promoting products, services, or brands by highlighting traits, values, and ideals traditionally considered feminine or masculine. This approach uses specific messages and aesthetics to attract and engage women or men as target audiences.
Marketing femininity appeals to qualities such as empathy, gentleness, and care. Products are often promoted in contexts that emphasize nurturing, relationships, and well-being.
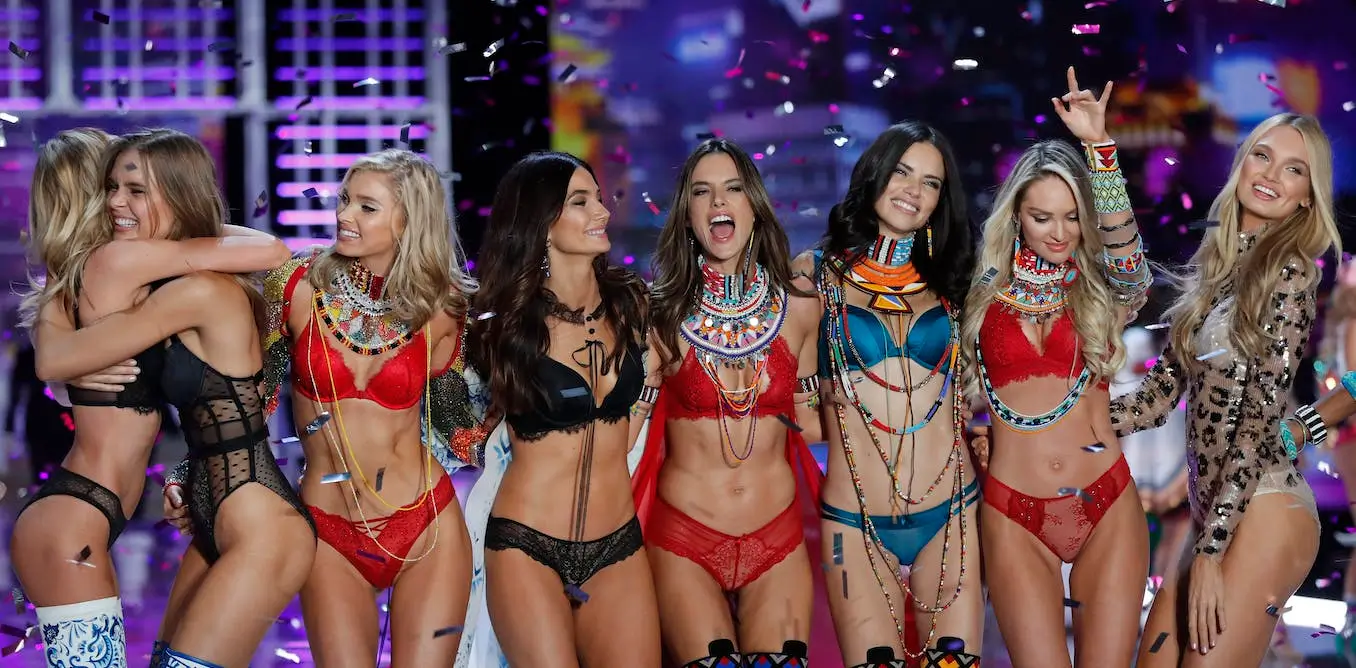

Example: Victoria’s Secret campaigns often rely on promoting stereotypical beauty standards. The brand’s “Angels” campaigns present women as symbols of elegance and sensuality.
Marketing masculinity, on the other hand, focuses on values like strength, independence, and achievement. Advertisements often emphasize themes of survival, competition, and leadership. Products are frequently labeled “for men.”
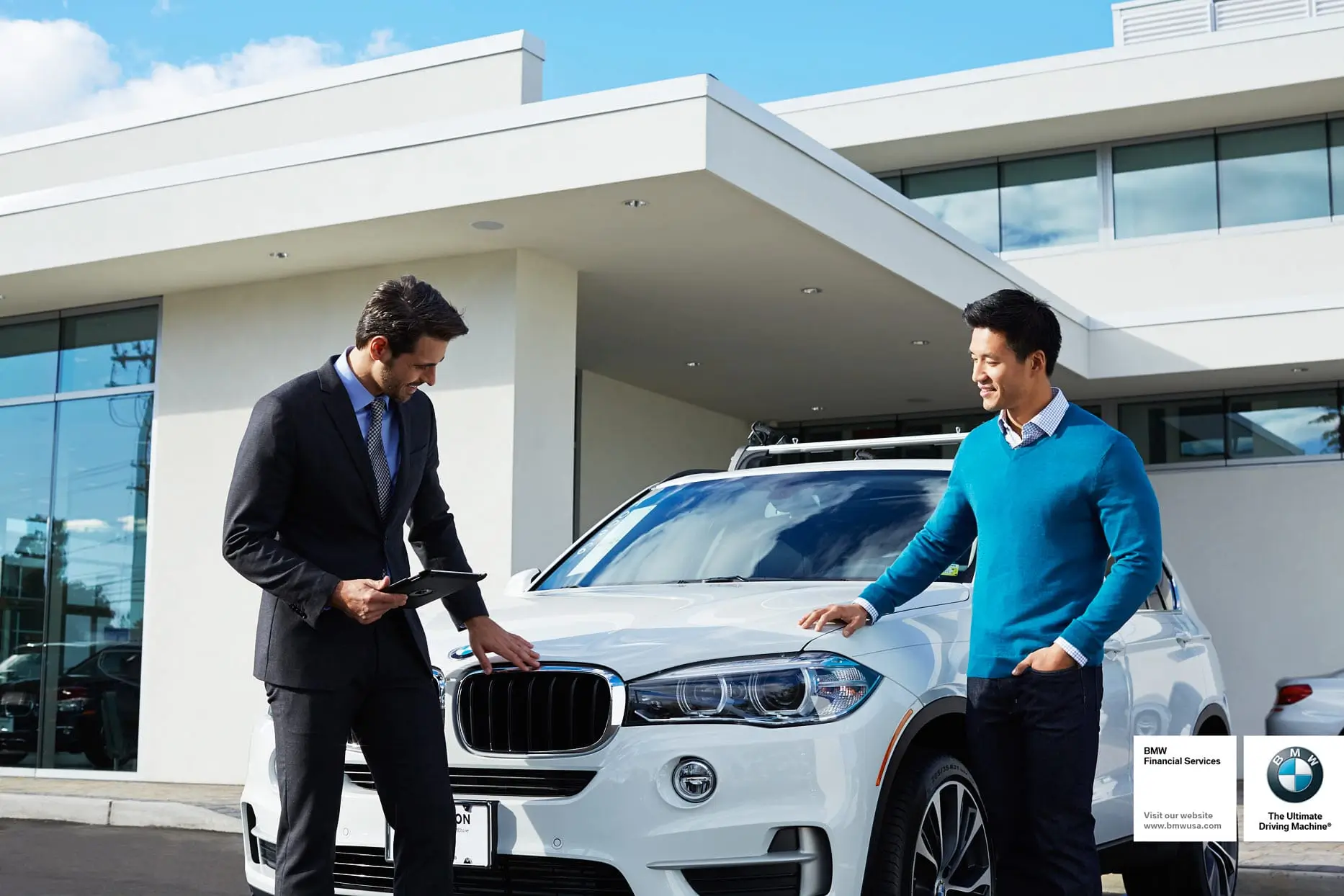

Example: BMW’s campaign “The Ultimate Driving Machine” promotes the image of men who enjoy speed, technology, and refined driving style.
Modern marketing increasingly integrates elements of both, aiming to avoid harmful stereotypes and promote equality. Women enjoy competition just as much as men, and not every woman identifies with the “lady” archetype from traditional ads. Likewise, men don’t want to be stereotypically lured by sex appeal—they may instead value subtle and emotional advertising messages.
Example: Microsoft’s “Empowering Us All” campaign represents a gender-neutral message aimed at all audiences. It highlights diverse people using Microsoft technology, emphasizing how tech can be accessible and useful for everyone.
Build an Effective Marketing Strategy with Rodin
Gender marketing is a powerful tool for boosting marketing effectiveness, but it requires caution to avoid reinforcing negative stereotypes and gender-based exclusions.
At Rodin Marketing Agency, we create creative ads for social media and search engines that reflect diversity and inclusion. We’ll help you build a positive brand image and strong relationships with customers. Effective gender marketing can translate into real market success for your brand.


